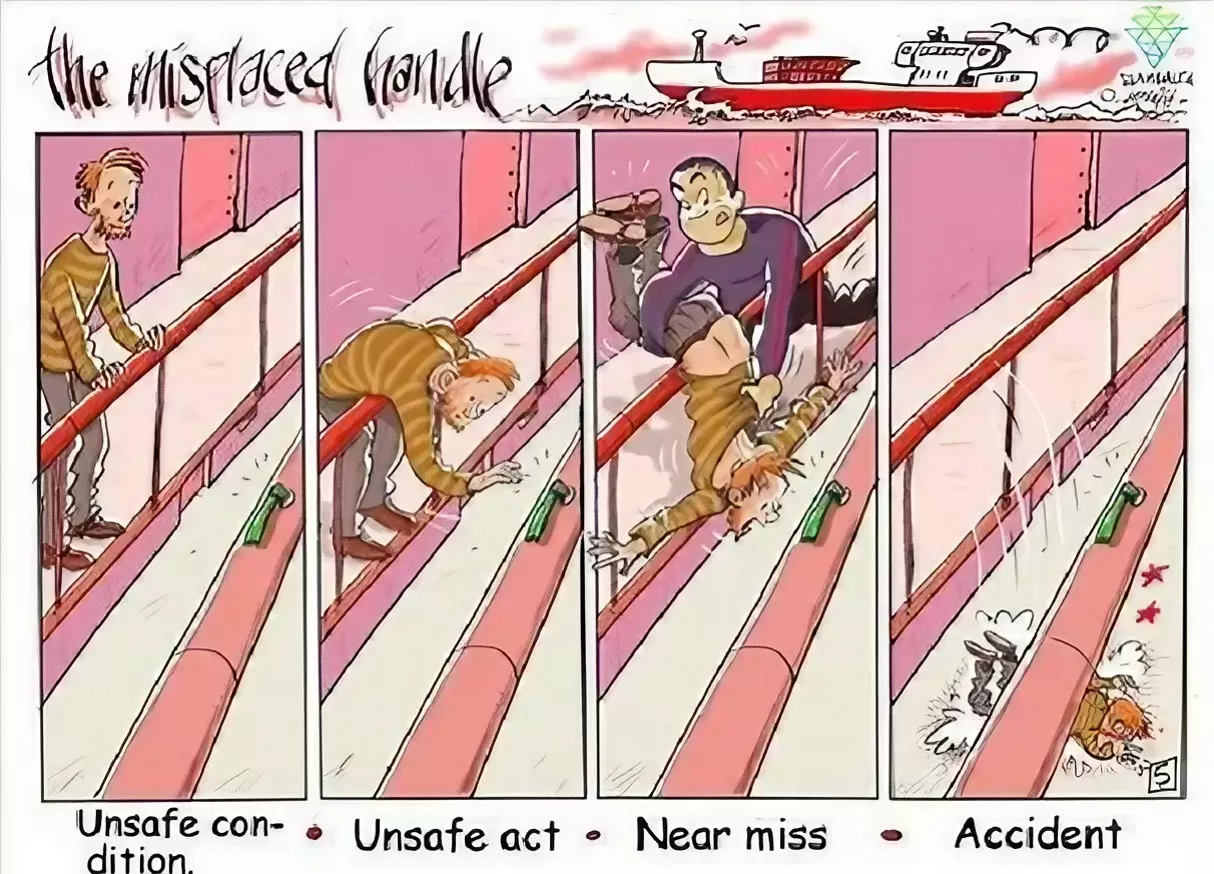
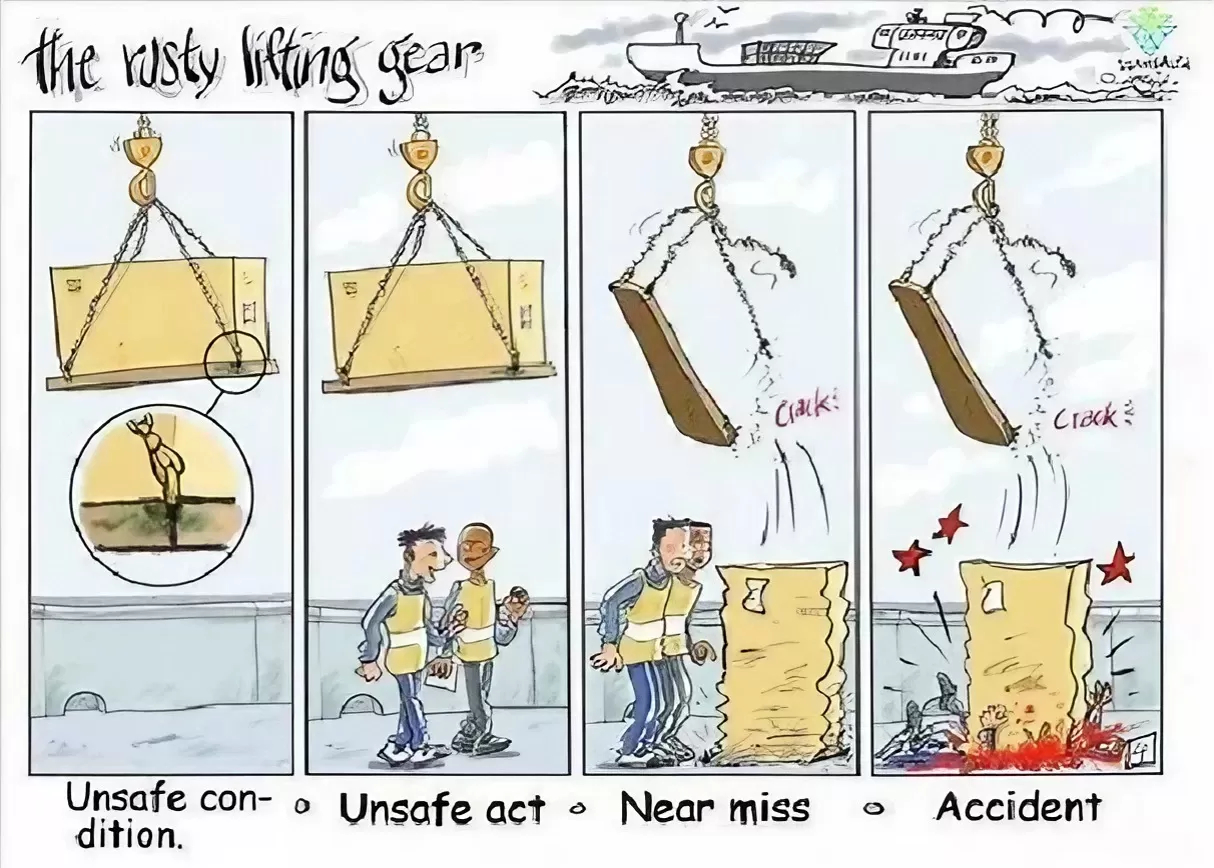
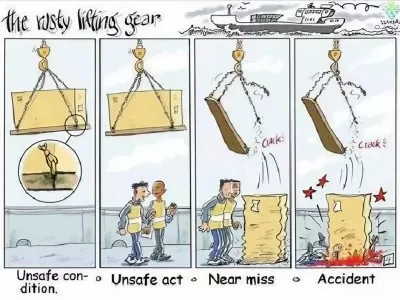
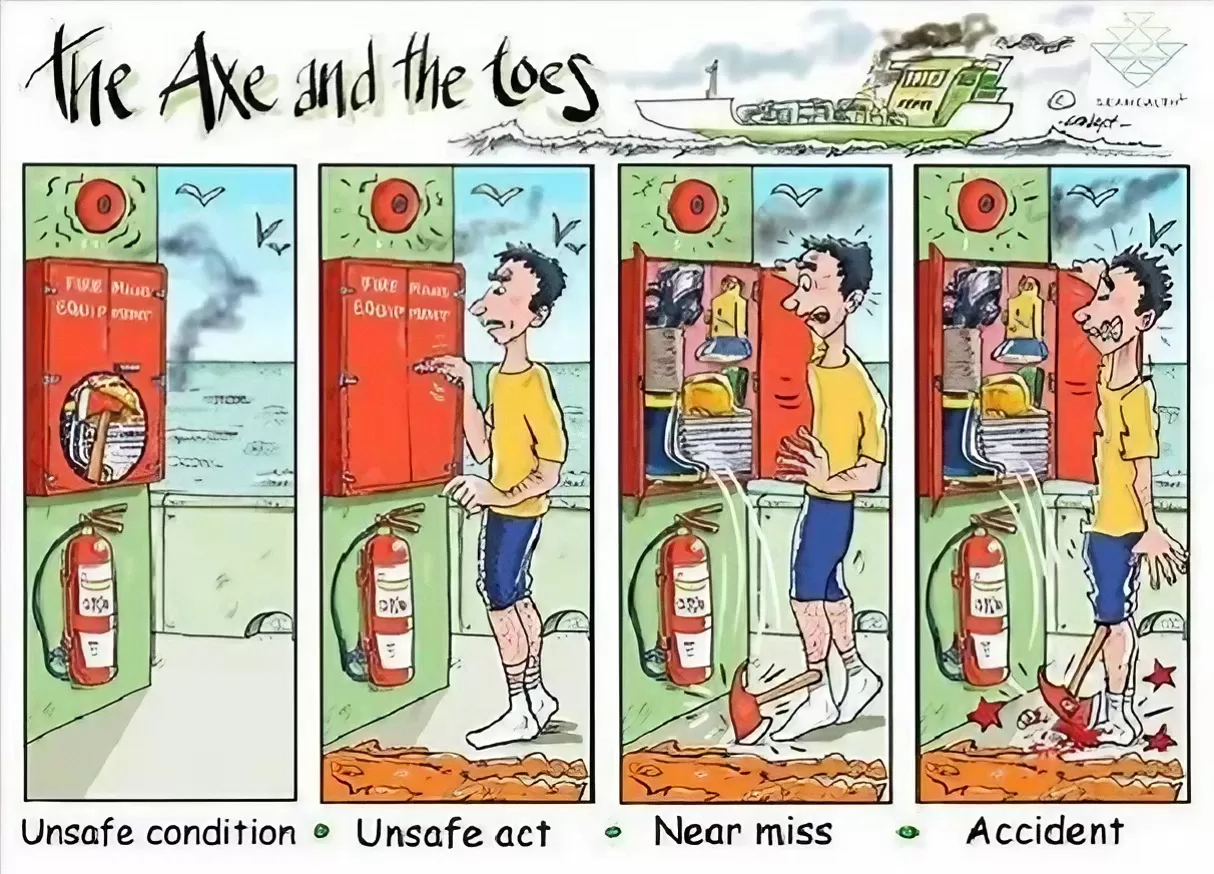
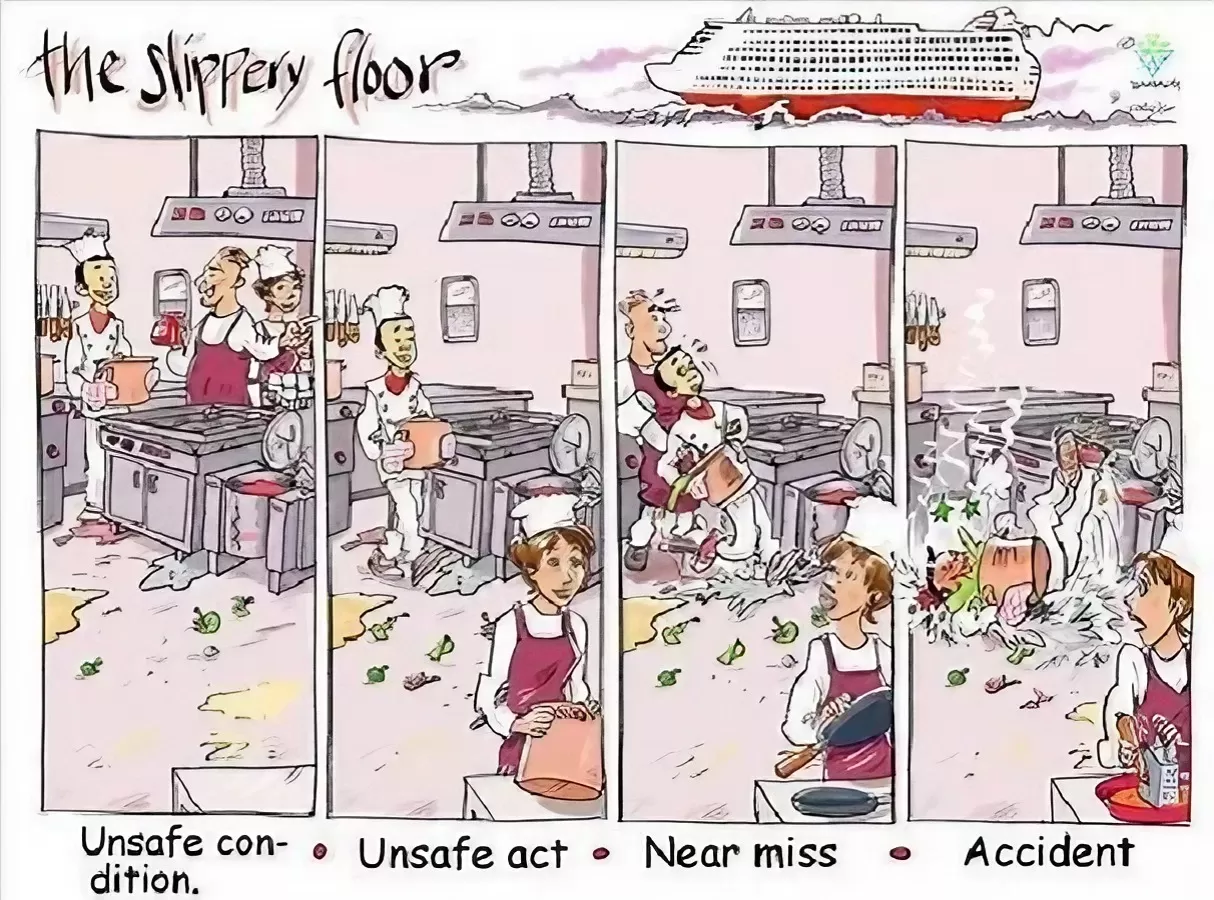
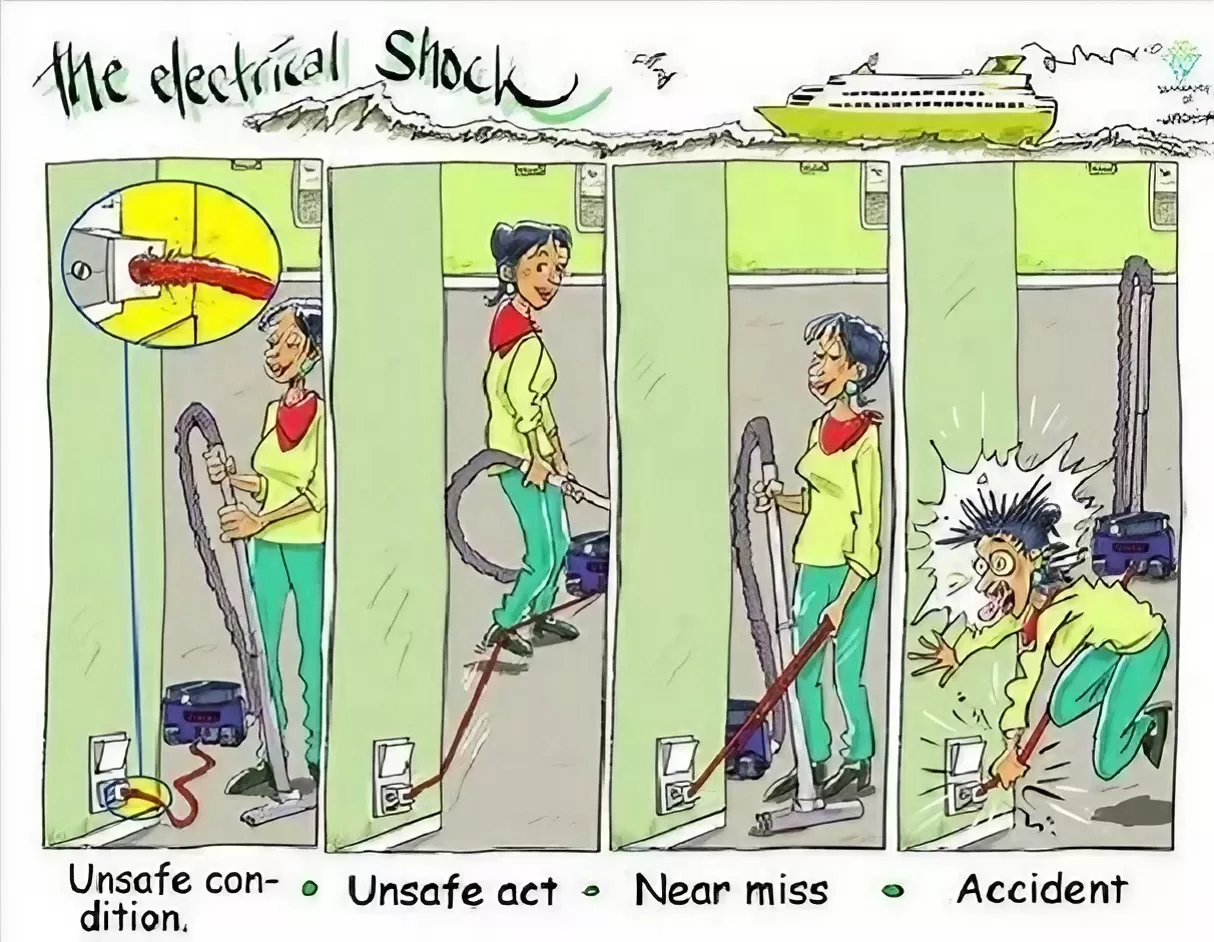
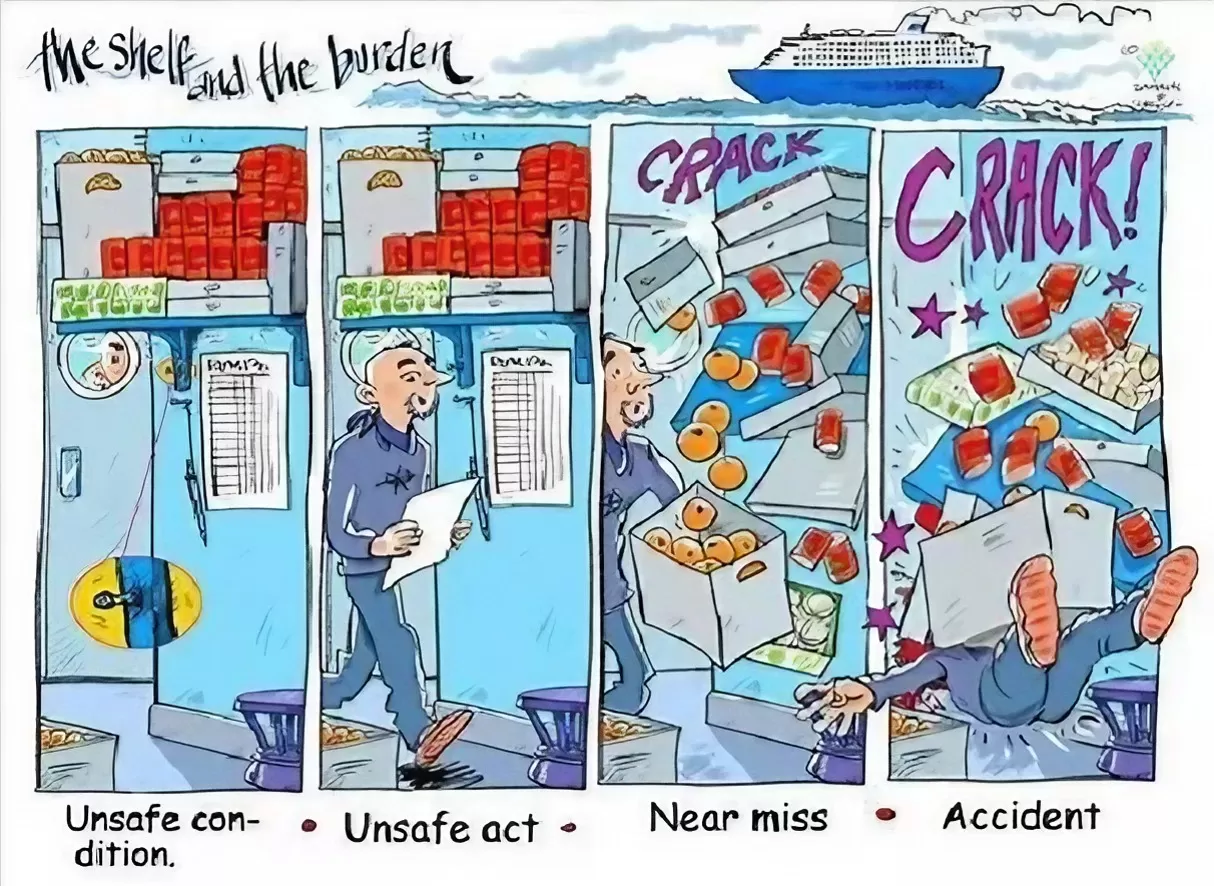
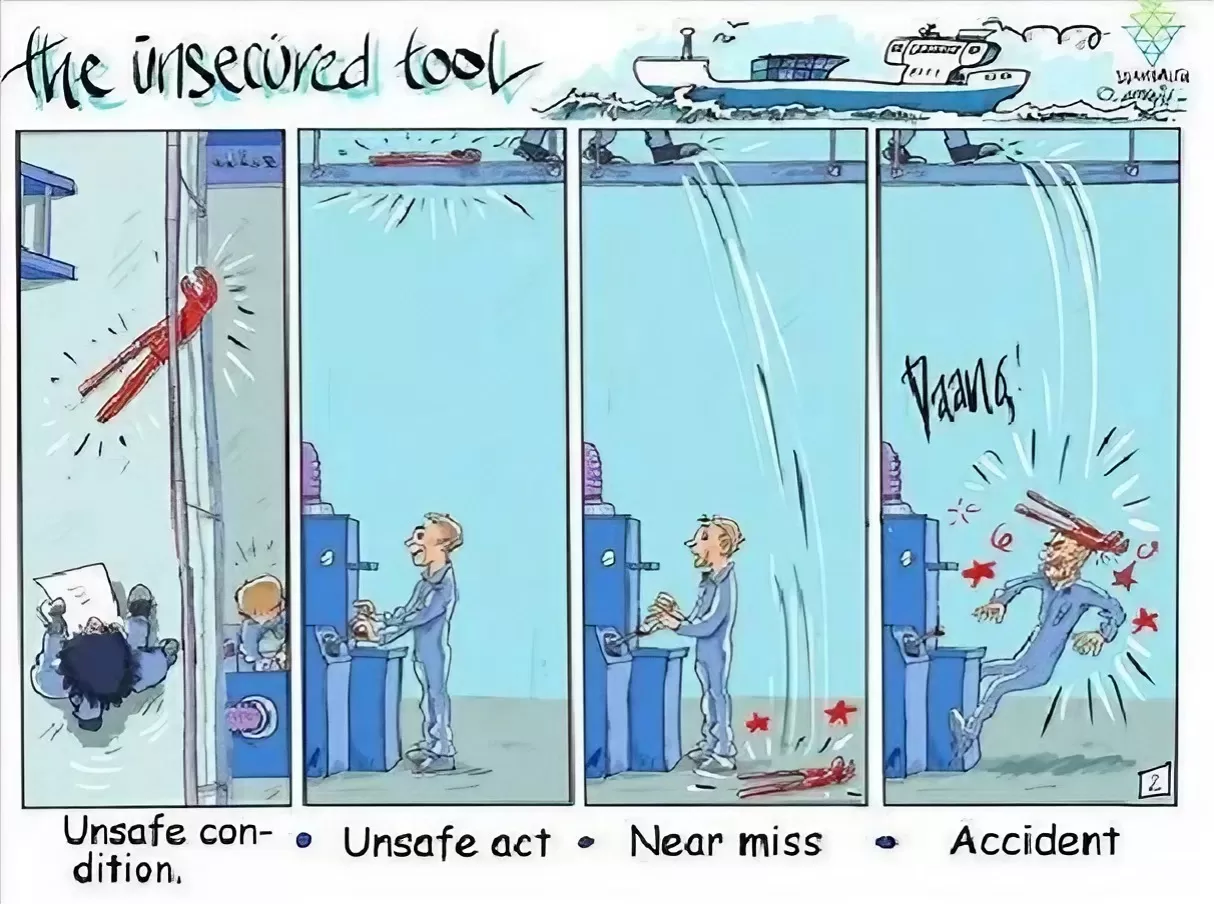
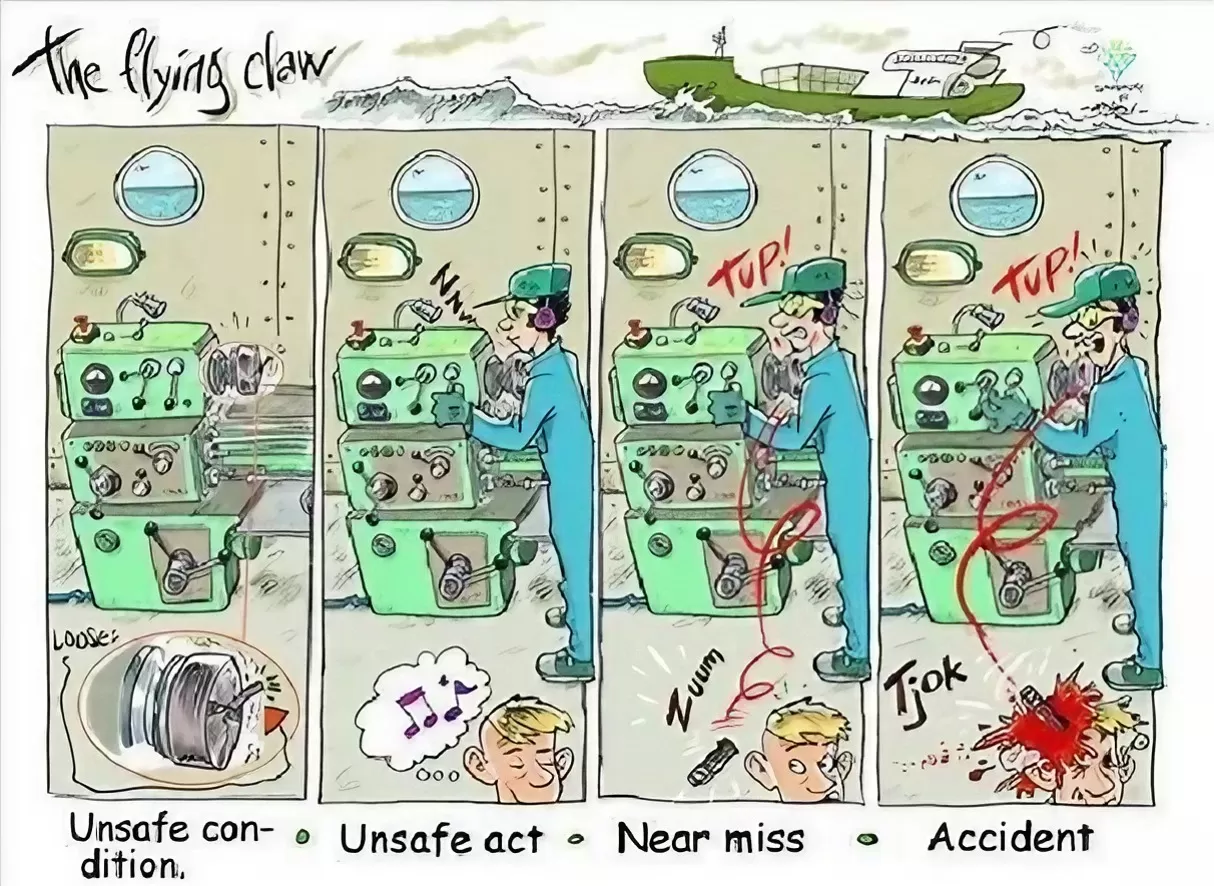
Type List-Head Protection Equipment
Prevent high-altitude falls and impact injuries to the head
Most Popular
-45%New


Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Blue Eagle 6 Points Suspension Hard Hat, Ratchet Cap Style, Electrical Helmet for Safety, Flexible Attachment for Construction, Home and General Head Protection
-30%New


Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
XYEHS Construction Adjustable Safety Helmet, Hard Hat with Rain Through, Impact Resistant, Half Brim Vented Cap with Premium Imported ABS Shell
XYEHS SR-1032 Safety Baseball Hat Style Bump Cap, Impact Resistant HDPE Shell Insert, EVA Cushion, Lightweight Safety Hard Hat, Reflective Strip, Short Brim, Breathable Hat Comfortable Head Protection Cap
-31%New
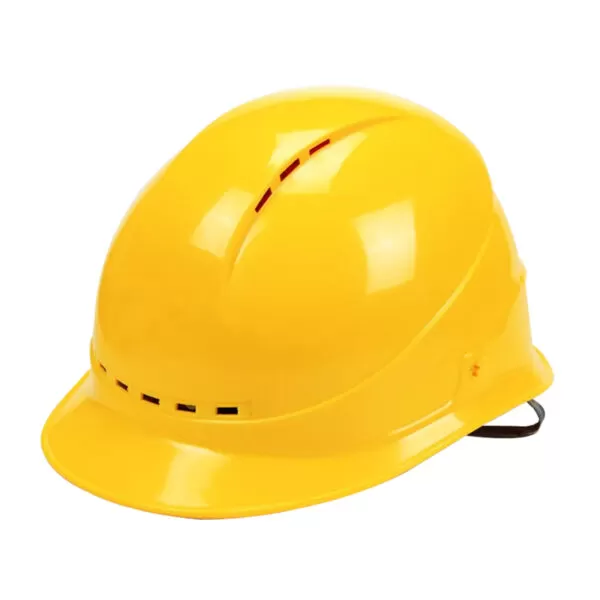
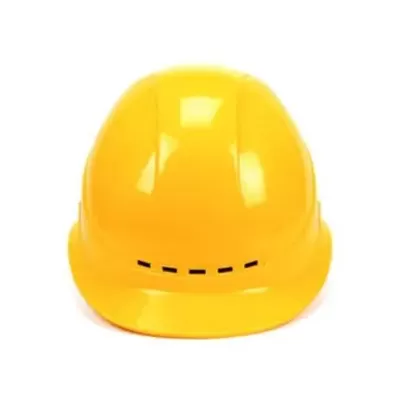


Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
 Hard Hat
Hard Hat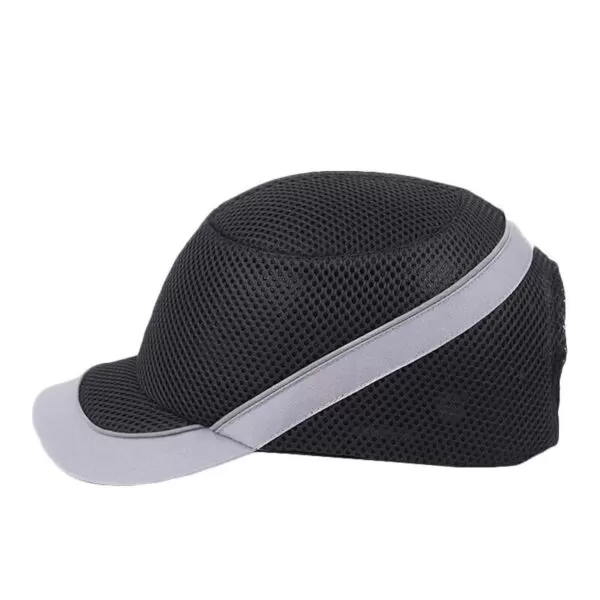 







 Face Shiled
Face Shiled  Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses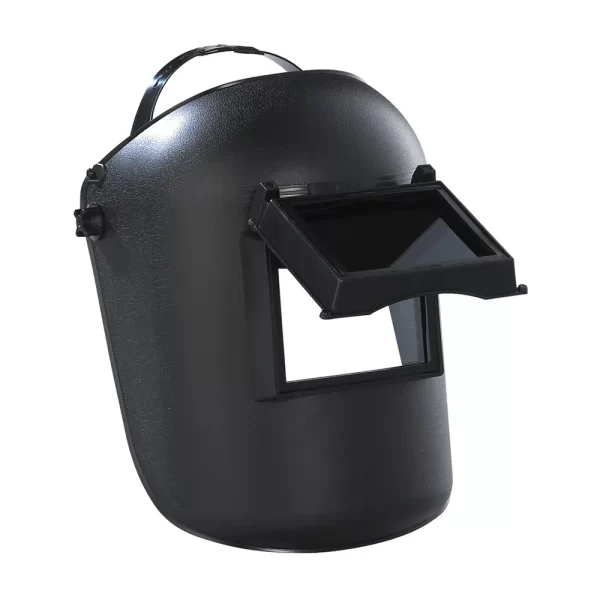 
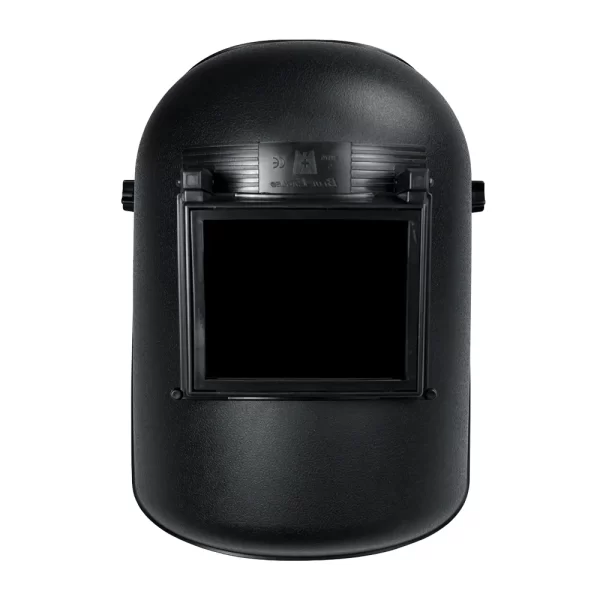
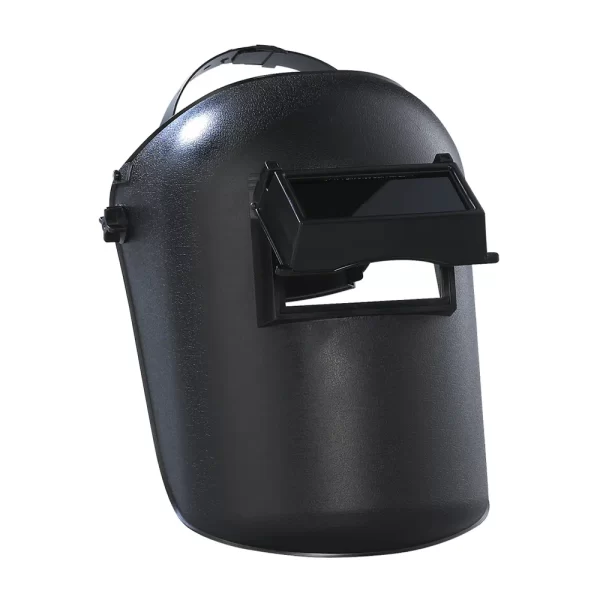
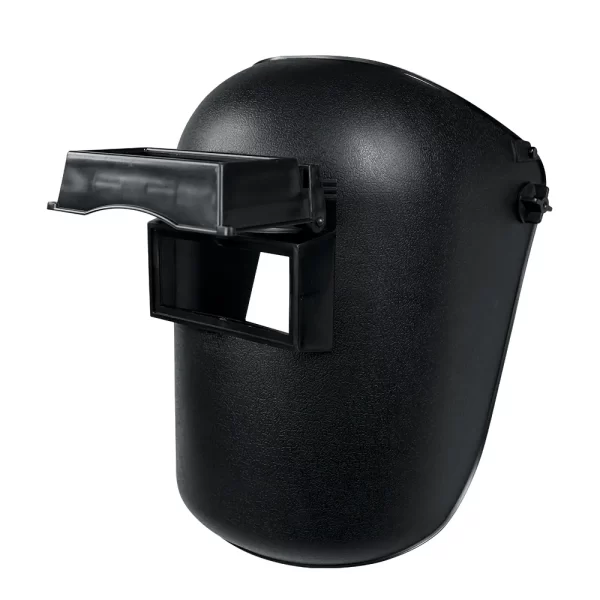










 Earmuffs
Earmuffs  Earplugs
Earplugs 







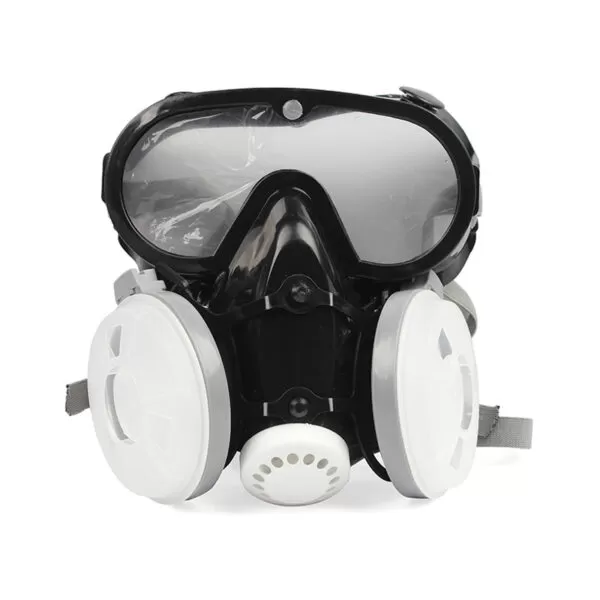
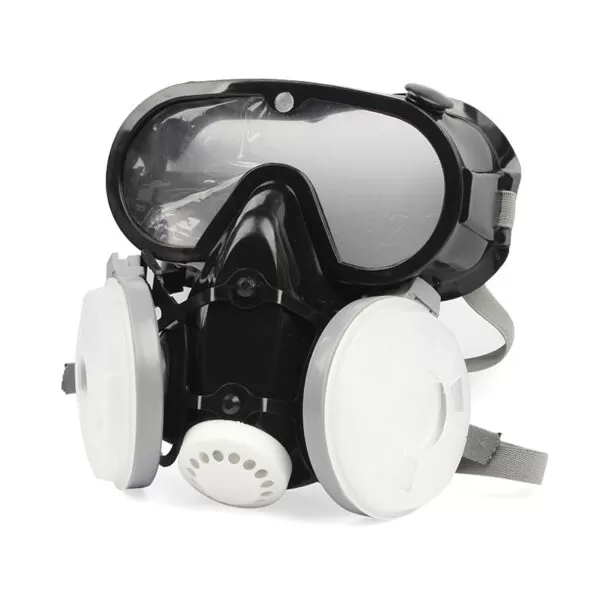
 Rubber Mask
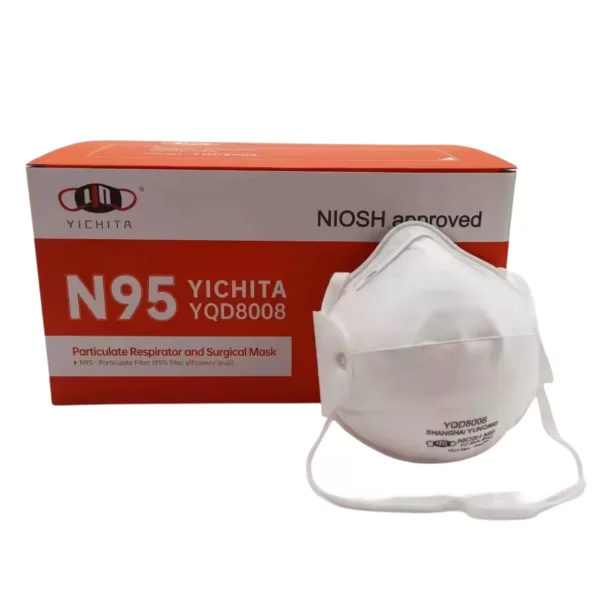
Rubber Mask  Mask
Mask 






 Work Gloves
Work Gloves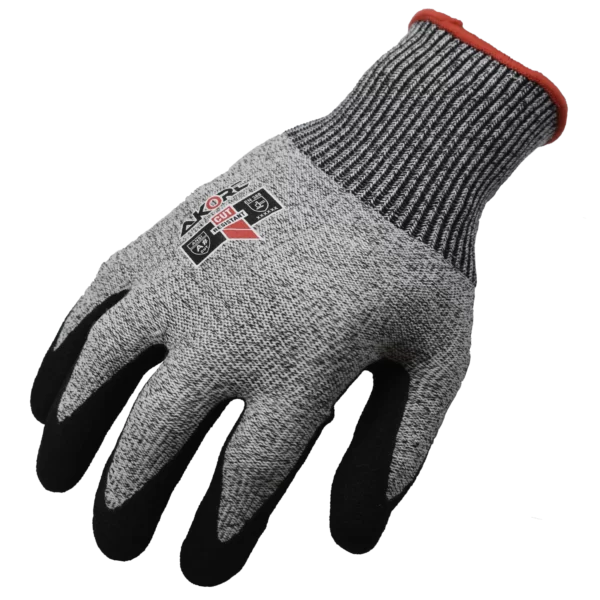 







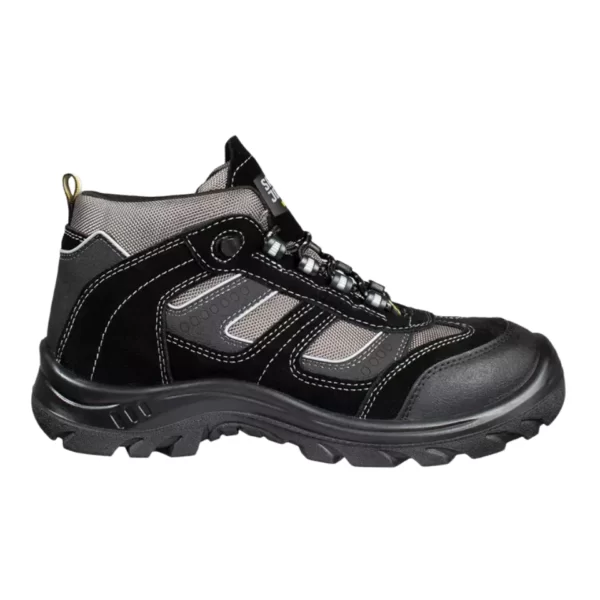
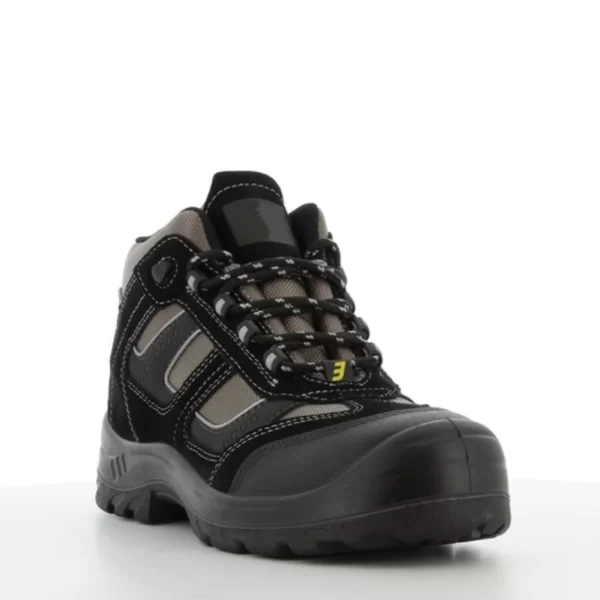
 Safety Shoes
Safety Shoes 






 Reflective Vest
Reflective Vest 






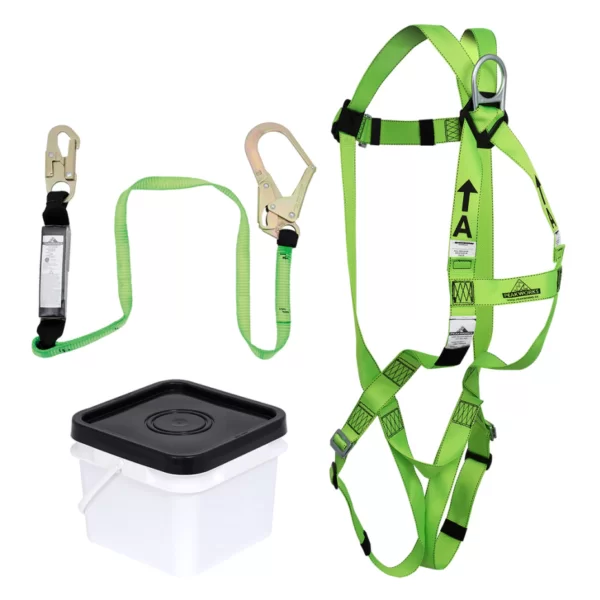
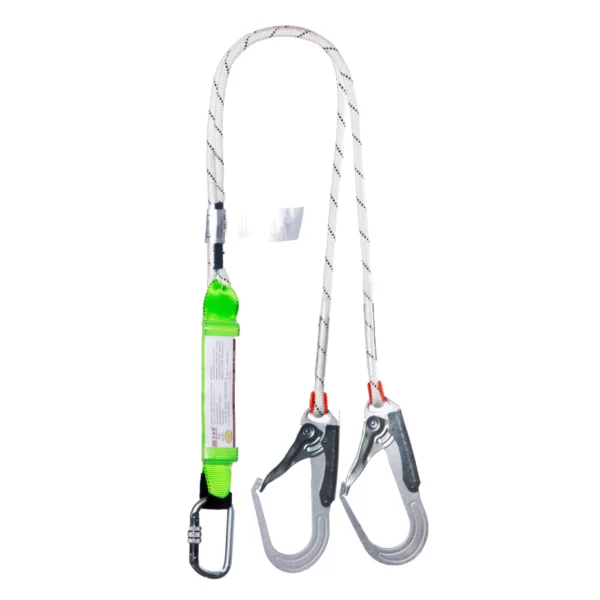
 Safety Belt
Safety Belt